Sign up for expert insights, industry trends, and key updates—delivered straight to you.

We leverage our vast industry experience of operational resilience engagements to assist you implement the guidance effectively on a day-to-day basis and to set future plans and strategies.
Regulatory Context
Following the Central Bank’s publication of Cross Industry Guidance on Operational Resilience in December 2021 firms are expected to comply with this guidance by December 2023.
Operational resilience concerns a firm’s ability to prevent, respond, recover and learn from operational disruptions and the Central Bank has outlined three pillars for application of the operational resilience guidance, providing a phased approach for the design and implementation of new frameworks.

Pillar 1: Identify & Prepare
Organisations are expected to:
- Prepare to address any vulnerabilities
- Assign owners for all critical business services
- Define impact tolerances, third party risks & map critical business services
Pillar 2: Respond & Adapt
Once a framework for guidance application is defined:
- Implement operating model to support overarching framework & embed operational resilience across the business.
- Integrate existing business initiatives including ongoing 3 Business Continuity Management & Incident Management
Pillar 3: Recover & Learn
Review lessons learned and use them to enhance the organisation’ capabilities:
- Operational resilience should be embedded in the culture
- Promotion of learning & continuous improvement as the understanding of operational resilience evolves
Key Considerations
Operational resilience is fundamental to meet the expectations of customers, business partners, and investors. Insurance firms must have plans in place to restore key products and services in the event of a service disruptions or outages and organisations should consider the following areas within their operational resilience framework.
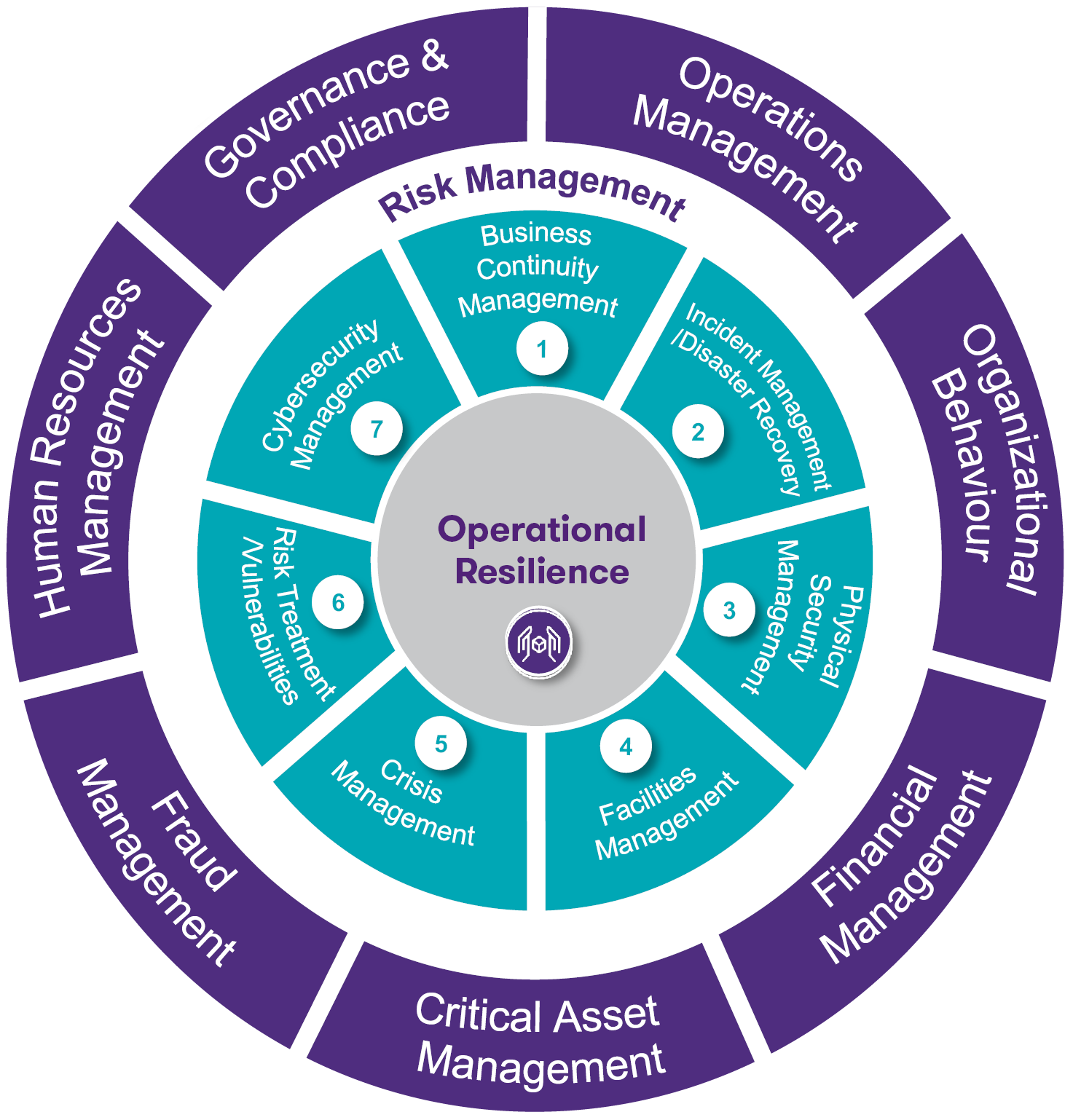
- Business Continuity Management: Understanding the criticality of each business area and identifying opportunities of recovery activities.
- Incident Management / Disaster Recovery: Identify and analyse potentially disruptive events to restore normal service operation as quickly as possible.
- Physical Security Management: Ensures the protection of physical access to company locations.
- Facilities Management: Ensures the protection of the organization’s physical facilities (e.g. buildings, energy and water supplies).
- Crisis Management: Identifies and responds to a threat, an unexpected event, or any negative disruption with the potential to impact business processes/services.
- Risk Treatment / Vulnerabilities: Identifies and responds to a threat, an unexpected event, or any negative disruption with the potential to impact business processes/services.
- Cybersecurity Management: Protects the company against external or internal threats to access to critical systems, networks and data.


